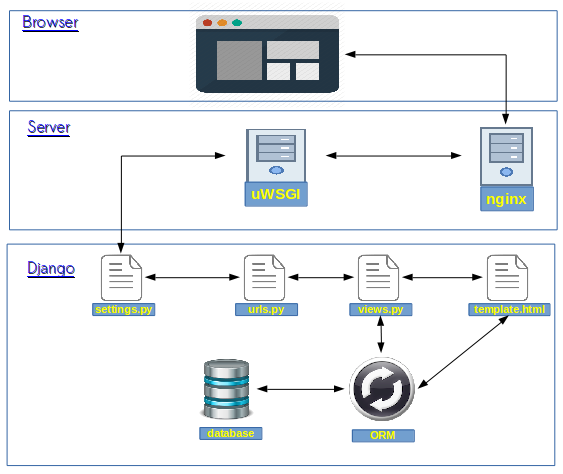
 |
| Architecture for django application |
1. Browser
2. Server
3. Django
1.Browser:
Browser(client) is responsible for sending data to the server and also responsible for receiving the response back.
2. Server:
- It receives the request from the browser, based on the request it gives response back. If we take an example of NGINX server. It can handle the 10,000 requests in a second based on the resources of the server(RAM, Processor).
- If it receives more than 10,000 requests in a second it creates another process to handle it.
- We can divide request resources in two types.
- 1. static resource
- 2. dynamic resource(It has to process the data based on request to provide resource)
- If browser request for the static resources like images/css/javascript/etc, then NGINX serves the request without sending it to the uWSGI server.
- If browser requests for a dynamic request then NGINX passes it to the uWSGI to process the request.
- At this stage NGINX acts like a reverse proxy server. A reverse proxy server is a type of proxy server that typically sits behind the firewall in a private network and directs browser/client requests to the appropriate back-end server(uWSGI).
- Advantages of reverse proxy server are Load balancing, Web acceleration, Security and anonymity.
3. Django
- Django layer comes into the picture when request passed from nGINX to the uWSGI it takes the request middlewares from the settings and applies on the request to modify request.
- After applying the request middlewares it sends the request to url dispatcher. Url dispatcher is responsible for dispatching the request to a view based on the url pattern
- Here we implement the business logic. We access the database resources by writing Django Queries.
- The query passes to the ORM(Object Relation Mapper). ORM converts the django query into SQL(Structured Query Language) query and hits the database (MySQL/Postgres,etc). Database returns the query results in a relational table. ORM again converts these relational data into django queryset and returns back to the view.
- View passes the context(data that's retrieved from the database) to the template.
- Template renders the content with context data and forms the Response(HTML/XML/JSON/etc.)
- Again response middlewares which are defined in settings will apply and modifies the request and sends the response to the Browser(Client).
Django
